UAC Levels & Windows User Account Control Settings
Table of Contents
When the AutoElevate agent is installed on a computer, it reads the UAC registry values that are currently set and reports the "UAC Levels" to the Admin Portal for you to evaluate.
This document maps out which values equate to which levels & what that means in terms of functionality in Windows. (See this Microsoft document for specific UAC information)
AutoElevate's "UAC Levels" correspond to the "Slider" positions in the "User Account Control Settings Screen".
Below is a full description of each level, followed by a section that outlines what Registry keys correspond to the different values found in the Admin Portal and what Registry keys get set when you use one of the UAC "Actions" on a Computer.
Windows User Account Control Settings - Slider Positions & Feature Descriptions
Administrator Slider Positions
Level 4
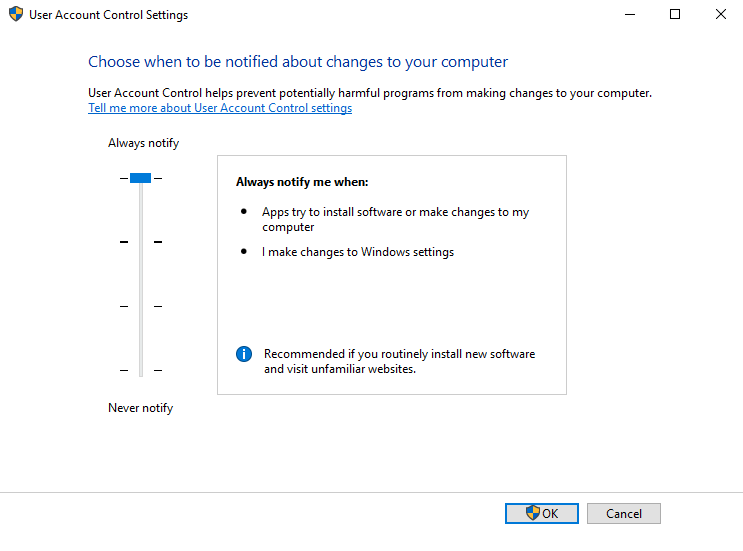
Level 3
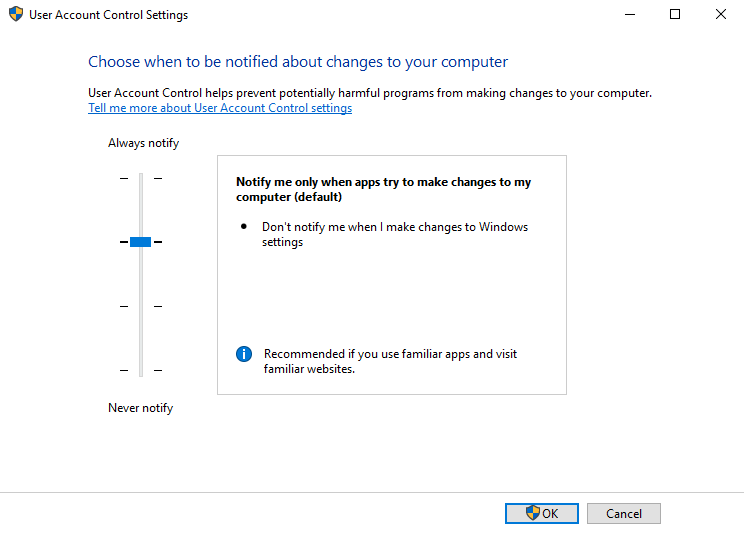
Level 2
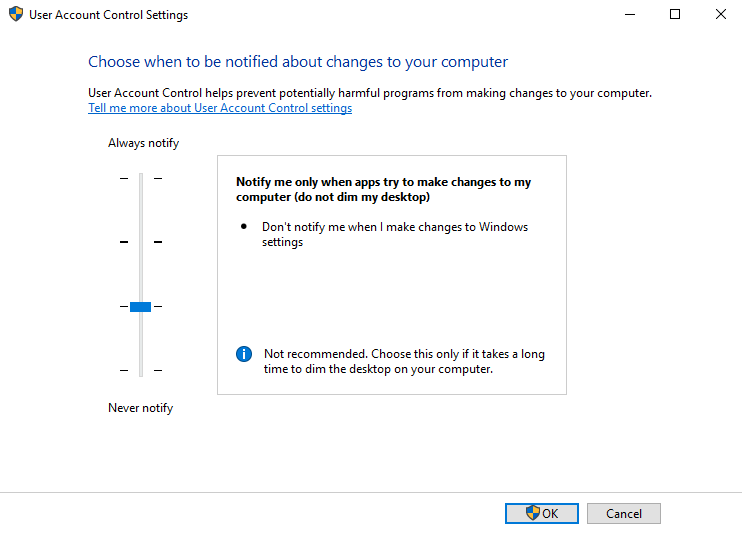
Level 1 (Off)
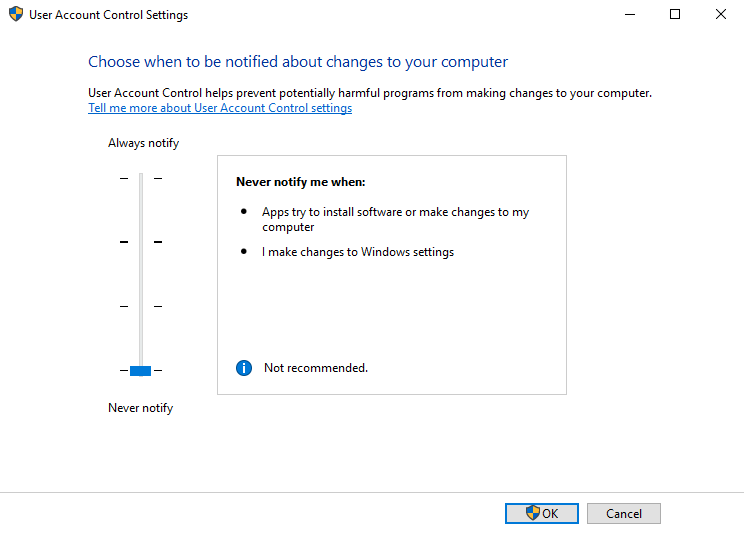
Standard User Slider Positions
Level 4
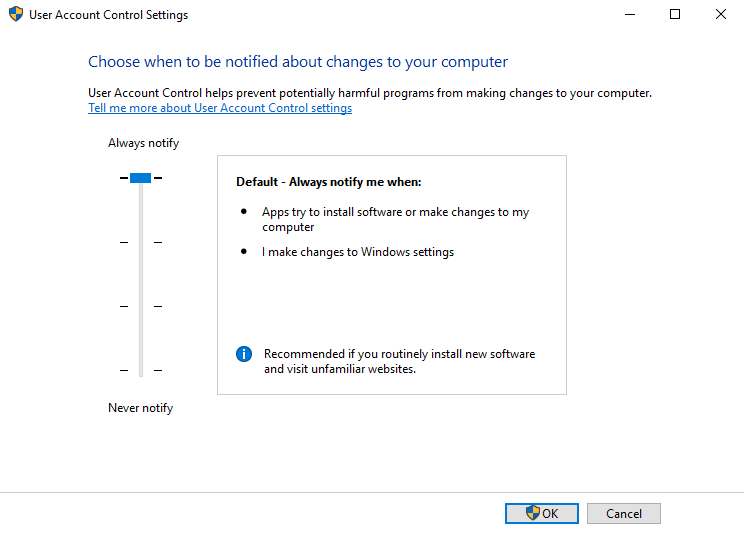
Level 3
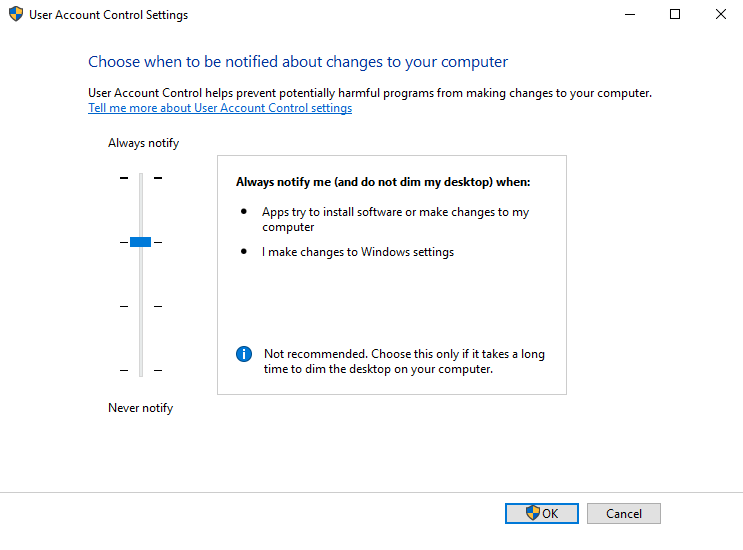
Level 2
It cannot set for a Standard User
Level 1
It cannot be set for a Standard User
Admin Portal Grid Value to Registry Mapping
| Grid Values | Registry Keys |
| UAC Status - Off | EnableLUA = 0 |
| UAC Status - On (Dimmed) |
EnableLUA = 1
PromptOnSecureDesktop = 1 |
| UAC Status - On (Not Dimmed) |
EnableLUA = 1
PromptOnSecureDesktop = 0 |
|
UAC Status - On (Maximum)
UAC Admin Level - Level 4
UAC User Level - Level 4 |
EnableLUA = 1
PromptOnSecureDesktop = 1
ConsentPromptBehaviorAdmin = 1, 2, 3, OR 4
ConsentPromptBehaviorUser = 1 |
|
UAC Status - On (Dimmed) UAC Admin Level - Level 3 UAC User Level - Level 4 |
EnableLUA = 1 PromptOnSecureDesktop = 1 ConsentPromptBehaviorAdmin = 5 ConsentPromptBehaviorUser = 1 |
|
UAC Status - On (Not Dimmed) UAC Admin Level - Level 4 UAC User Level - Level 3 |
EnableLUA = 1 PromptOnSecureDesktop = 0 ConsentPromptBehaviorAdmin = 3 OR 4 ConsentPromptBehaviorUser = 3 |
|
UAC Status - On (Not Dimmed) UAC Admin Level - Level 2 UAC User Level - Level 3 |
EnableLUA = 1 PromptOnSecureDesktop = 0 ConsentPromptBehaviorAdmin = 5 ConsentPromptBehaviorUser = 3 |
|
UAC Status - On (Not Dimmed) UAC Admin Level - Level 1 (Off) UAC User Level - Level 3 |
EnableLUA = 1 PromptOnSecureDesktop = 0 ConsentPromptBehaviorAdmin = 0 ConsentPromptBehaviorUser = 3 |
Admin Portal Action to Registry Mapping
| Action | Registry Keys |
|
UAC Settings - Set to On (Not Dimmed) UAC Admin Level - Level 2 UAC User Level - Level 3 |
EnableLUA = 1 PromptOnSecureDesktop = 0 ConsentPromptBehaviorAdmin = 5 ConsentPromptBehaviorUser = 3 |
|
UAC Settings - Set to On (Dimmed) UAC Admin Level - Level 3 UAC User Level - Level 4 |
EnableLUA = 1 PromptOnSecureDesktop = 1 ConsentPromptBehaviorAdmin = 5 ConsentPromptBehaviorUser = 1 |
|
UAC Settings - Set to On (Maximum) UAC Admin Level - Level 4 UAC User Level - Level 4 |
EnableLUA = 1 PromptOnSecureDesktop = 1 ConsentPromptBehaviorAdmin = 2 ConsentPromptBehaviorUser = 1 |
| UAC Settings - Set to Off |
EnableLUA = 0 PromptOnSecureDesktop = 0 ConsentPromptBehaviorAdmin = 0 ConsentPromptBehaviorUser = 3 |
Troubleshooting
Group policies and settings that may affect the UAC and prevent AutoElevate agent from processing an elevation normally:
1. User Account Control: Admin Approval Mode for the Built-in Administrator account
- Description: Controls whether the built-in Administrator account runs in Admin Approval Mode.
- Location: Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Security Options
-
Setting:
- Enabled: Admin Approval Mode is required.
- Disabled: The built-in Administrator operates in unrestricted mode.
2. User Account Control: Behavior of the Elevation Prompt for Administrators in Admin Approval Mode
- Description: Determines the behavior of the elevation prompt for administrators.
- Location: Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Security Options
-
Options:
- Prompt for consent: Prompts for user consent.
- Prompt for credentials: Prompts for credentials.
- Elevate without prompting: Automatically elevates without prompting.
3. User Account Control: Behavior of the Elevation Prompt for Standard Users
- Description: Controls how the system responds when standard users attempt to perform tasks that require elevation.
- Location: Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Security Options
-
Options:
- Prompt for credentials: Prompts for an admin password.
- Automatically deny elevation requests: Denies the request without prompting.
4. User Account Control: Detect Application Installations and Prompt for Elevation
- Description: Controls whether the system prompts for elevation when it detects an application installation.
- Location: Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Security Options
-
Setting:
- Enabled: Prompts when an application installation is detected.
- Disabled: Application installations proceed without a UAC prompt.
5. User Account Control: Only Elevate Executables that are Signed and Validated
- Description: Controls whether only executables that are signed and validated are allowed to run with elevated privileges.
- Location: Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Security Options
-
Setting:
- Enabled: Only signed executables are allowed to elevate.
- Disabled: Any executable can request elevation.
6. User Account Control: Run All Administrators in Admin Approval Mode
- Description: Controls whether all users, including administrators, must use Admin Approval Mode.
- Location: Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Security Options
-
Setting:
- Enabled: All administrators must go through Admin Approval Mode.
- Disabled: Administrators can perform tasks without prompts.
7. User Account Control: Switch to the Secure Desktop When Prompting for Elevation
- Description: Determines whether the elevation prompt appears on a secure desktop, isolated from the user environment to prevent spoofing.
- Location: Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Security Options
-
Setting:
- Enabled: The prompt appears on the secure desktop.
- Disabled: The prompt appears on the regular desktop.
8. User Account Control: Virtualize File and Registry Write Failures to Per-user Locations
- Description: Controls whether UAC virtualizes write failures to per-user locations for applications that are not UAC-compliant.
- Location: Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Security Options
-
Setting:
- Enabled: UAC virtualizes the file and registry writes.
- Disabled: Virtualization is not allowed.
9. Enable Passwordless Experience
- Description: A Windows 11 security policy that hides password options in most sign‑in and in‑session authentication scenarios.
- Location: Intune Admin Center → Devices → Configuration profiles > Create profile > Settings catalog > Authentication > Enable Passwordless Experience
-
Setting:
- Enabled: Hides password-based authentication options during in-session prompts (e.g., UAC elevation, password manager use).
- Disabled: Windows behaves normally: Users can elevate, authenticate, or change their password using traditional password prompts.